Computer-Navigated and Robotic Total Knee Replacement
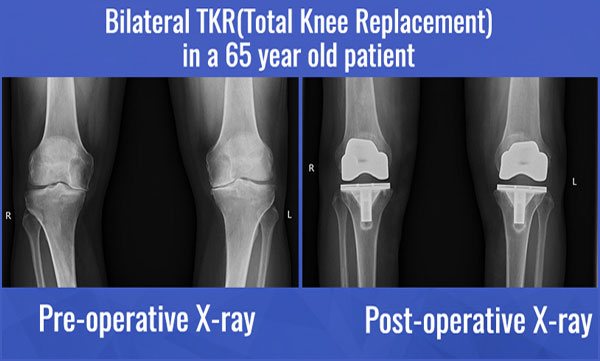
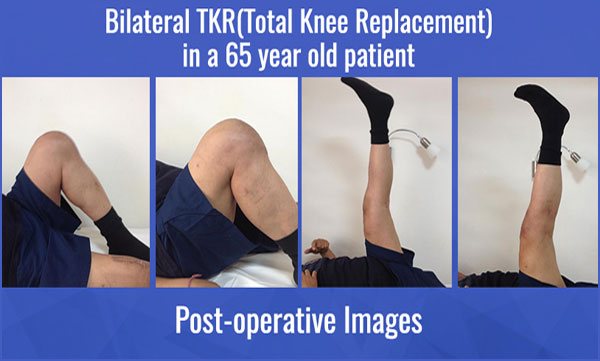
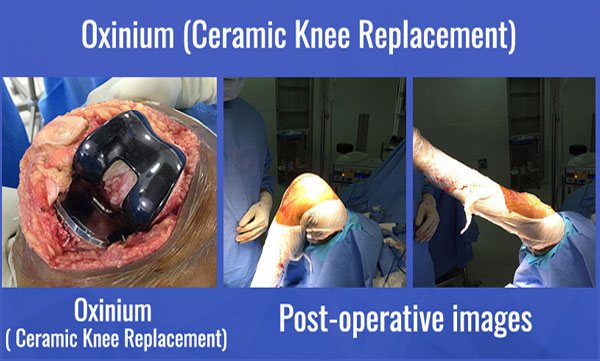
Total knee arthroplasty, i.e., abbreviated as TKA is a well-known method opted for Total Knee Replacement. TKA is a process followed by the surgeons to improve the functioning of knees for the patients suffering from osteoarthritis. It is highly recommended by the doctors as it quickly helps in relieving severe pain. The aim considered while performing this surgery is to avail the respective patient with a well-aligned prosthesis that eventually helps in getting properly balanced ligaments. After the surgery, the wear and tear risks get minimized, and that is how the patient feels instant relief in his/her pain.
The total knee replacement surgery helps the suffering patients to a greatest extent, but to reduce some malfunctioning and control the surgical variables, robotics and computer navigation provisions have been accepted. Opting for these advanced techniques make the surgery even more successful and consistent.
Improvements Introduced Through Computer Navigated and Robotic Tools
Computer-based navigation tools are being utilized to better up implant alignment as well as to upgrade clinical results. Most of the studies have exhibited that the acceptance of navigation involves lesser radiographic radiations. In many of the reviews, radiographic results have been compared in between TKA (usual) and TKA done using automated solutions.
Though, there is no comparison is short-term and long-term research done regarding the same, but the short-term studies have revealed that computer-navigated and robotic total knee replacement has improved the alignment functioning to a significant extent.
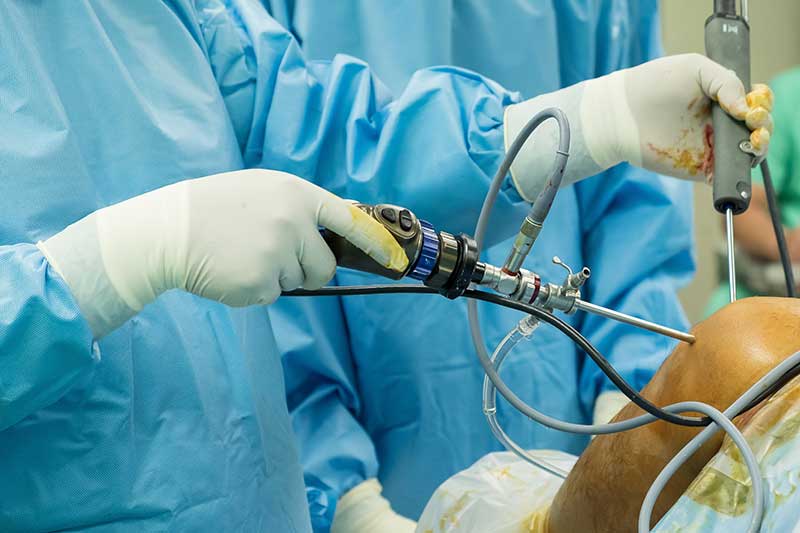
While surgical computer navigation helps in improving the tactics associated with implanting, the robotic tools and techniques assist in refining the operational execution. In inclusion with the surgical navigation tools, robotics associated with surgical tactics may improve precision in implanting and placement.
As of now, robotic techniques are being used in UKA, i.e., uni-compartmental knee arthroplasty. The usage of these techniques has proven that the robotic tools are approx. Three times more accurate than the conventional methods.
Computer navigation, as well as robotic tools, may prove to be extremely helpful in lower-limb alignment, implant positioning, implant designing, implant fixing, and soft tissue balance, etc.
Associated Techniques & Instruments
CAOS, i.e., Computer-Aided Orthopedic Surgery involves all the techniques, which are used to improve the surgical field’s visibility and executes better accuracy because of the use of robots and various navigation systems. Surgical navigational systems are preferable options in relation to knee surgery as these systems improve the efficiency of the surgeries without introducing any drawbacks. Plus, the surgical navigation systems make you get rid of the costing associated with robots.
Navigation systems offer all the information on a real-time basis concerning with the positioning of the various surgical instruments related to a virtual representation of the object that is about to be operated.
The essential component associated with the navigation computer on to which the system remains dependent is the coordination among the received data, mathematical interpretations & the display of resultant data on the screen (monitor). The components other than that are the tracking systems as well as, the dynamic reference-bases that shows the targeted objects of navigation.